Advancements and Applications of Trenchless Reamers in Modern Pipeline Rehabilitation

Introduction to Trenchless Reamers
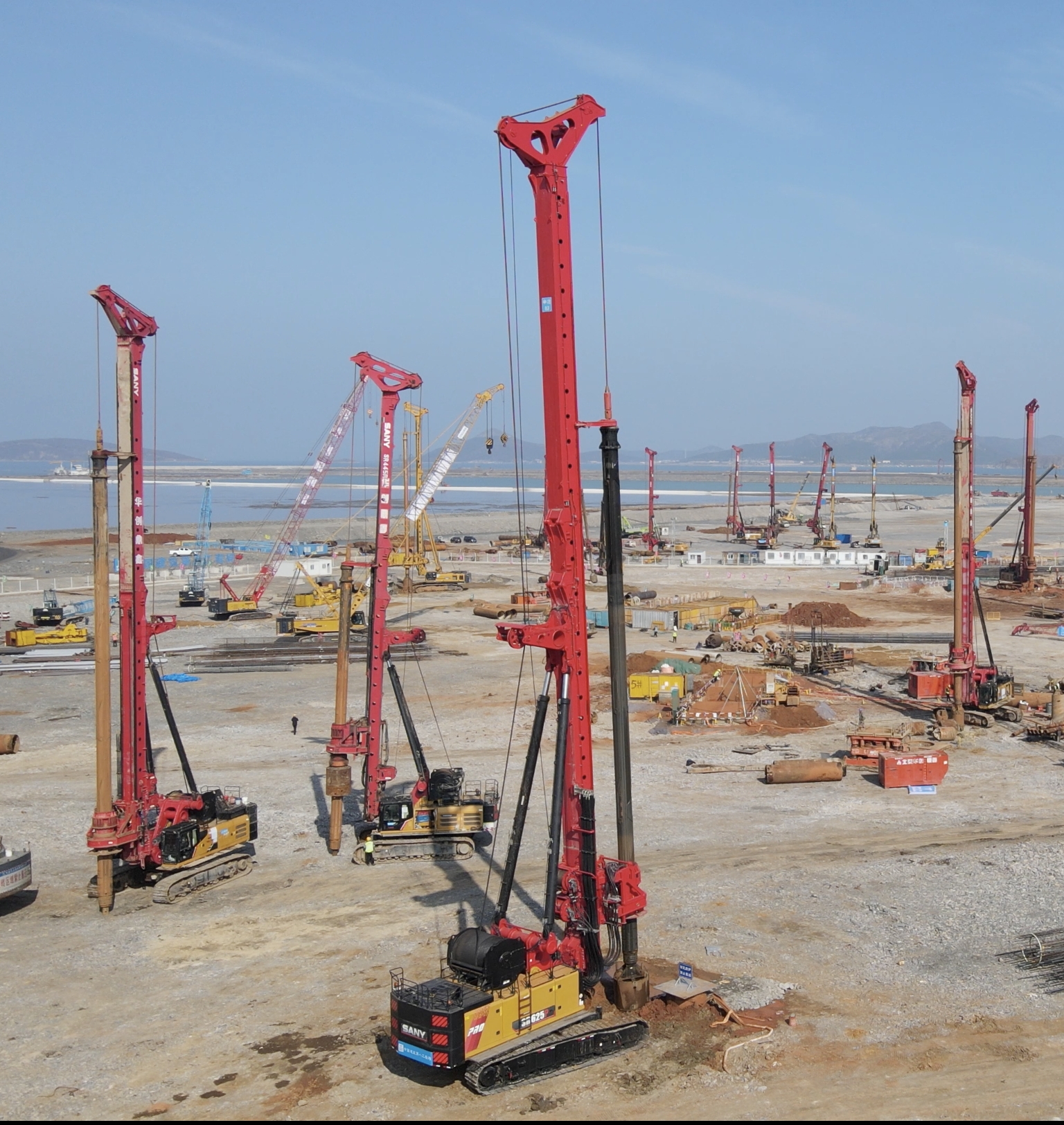
Trenchless reamers are specialized tools used in pipeline rehabilitation to enlarge or reshape existing pipes without extensive excavation. Unlike traditional methods that require digging trenches, these devices minimize surface disruption, making them ideal for urban environments. Key advantages include reduced labor costs and faster project completion, which are critical in densely populated areas. For instance, in a recent water main upgrade in New York City, the use of a trenchless reamer cut downtime by 40% compared to conventional approaches.
Technical Mechanisms and Design
The core technology of trenchless reamers involves a cutting head equipped with hardened steel or carbide teeth that grind away pipe obstructions or enlarge diameters. These tools are typically powered by hydraulic or pneumatic systems, allowing precise control over reaming operations. Common parameters include reaming diameters ranging from 4 to 48 inches and torque capacities up to 10,000 ft-lbs, depending on the pipe material and soil conditions. In a sewer line project in Chicago, engineers used a reamer with a 12-inch diameter capability to handle cast iron pipes, achieving a smooth bore with minimal residue.
Material Compatibility and Performance
Trenchless reamers are designed to work with various pipe materials, such as PVC, clay, and concrete. The selection of cutting teeth and feed rates must match the pipe's hardness to avoid damage. For example, softer materials like PVC require lower torque settings to prevent cracking, while harder materials may need higher power inputs. Performance metrics, such as reaming speed and accuracy, are crucial; in a gas pipeline rehabilitation in Texas, a reamer achieved a precision of ±0.5 inches over a 500-foot section, ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Commercial Value and Cost Efficiency
From a business perspective, trenchless reamers offer significant cost savings by reducing excavation, restoration, and traffic management expenses. Studies show that trenchless methods can lower overall project costs by 20-30% compared to open-cut techniques. Additionally, faster deployment minimizes revenue loss for utilities and reduces public inconvenience. In a municipal project in Los Angeles, the adoption of trenchless reaming led to a 25% reduction in total expenses and a 50% shorter project timeline, enhancing stakeholder satisfaction.
Environmental and Safety Benefits
Environmental sustainability is another key advantage, as trenchless reamers limit soil disturbance and lower carbon emissions from heavy machinery. This aligns with green building certifications and regulatory requirements, such as those in California's environmental codes. Safety is also improved by reducing worker exposure to underground hazards. In a recent project in Seattle, the use of trenchless technology resulted in zero incidents related to trench collapses, highlighting its reliability.
Common Questions
What is the typical lifespan of a trenchless reamer?
The lifespan varies based on usage and maintenance, but with regular sharpening and proper storage, a high-quality reamer can last for 50-100 projects before needing replacement.
How do trenchless reamers handle different soil types?
They are adaptable to various soils; for instance, in sandy conditions, specialized stabilizers are used to prevent tool deviation, while in rocky soils, reinforced cutting heads are employed to maintain efficiency.